Sulfasalazine — what it treats and how to use it safely
If your doctor mentioned sulfasalazine, you probably want plain answers: what it does, what to watch for, and how to take it so it helps without surprises. Sulfasalazine is a medication commonly used for ulcerative colitis and rheumatoid arthritis. It reduces inflammation in the gut and joints and can slow disease activity when taken regularly.
How sulfasalazine works and who takes it
Sulfasalazine combines a sulfa drug (sulfapyridine) and 5‑aminosalicylic acid (5‑ASA). In the gut, bacteria break it down and the 5‑ASA part helps control inflammation. For rheumatoid arthritis, the exact anti‑inflammatory effects are less clear but it can reduce joint swelling and pain over weeks to months. Doctors prescribe it when steroids or other standard treatments aren’t enough or as part of a longer‑term plan to control symptoms.
Typical doses vary: for ulcerative colitis people often take 2–4 g per day, while for rheumatoid arthritis doses commonly run 1–3 g per day. Your prescriber will usually start low and raise the dose over several weeks to reduce side effects.
Side effects, monitoring, and practical tips
Common side effects include upset stomach, headache, loss of appetite, and a harmless yellow‑orange tint to urine or skin. Less common but serious problems include allergic reactions, liver issues, and blood count changes like low white cells. If you get fever, sore throat, unexplained bruising, dark urine, or yellowing of skin/eyes, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Your doctor should check blood tests before you start (CBC, liver tests, kidney function) and repeat them soon after starting—often at 2–4 weeks—and then periodically every 1–3 months while you’re on it. If you’re on methotrexate or pregnant or planning pregnancy, tell your doctor—sulfasalazine can affect folate levels, so folic acid is often recommended.
Practical tips: take doses with food to cut stomach upset, split the daily dose into two or three smaller doses, and store tablets dry. Protect your skin from strong sun—sulfasalazine can cause extra sun sensitivity. If you have a known sulfa allergy, don’t take this drug.
Interactions to note: it can affect warfarin dosing, and it may interact with other drugs that suppress bone marrow or the liver. Always run new prescriptions or over‑the‑counter meds by your pharmacist or doctor.
Expect benefits after several weeks to a few months for joint symptoms and quicker improvement for gut inflammation in some cases. If you don’t see improvement or side effects build up, your clinician can adjust dose, switch medications, or add supplements like folic acid. Ask questions and keep a simple log of symptoms and side effects—this helps your care team adjust treatment faster.
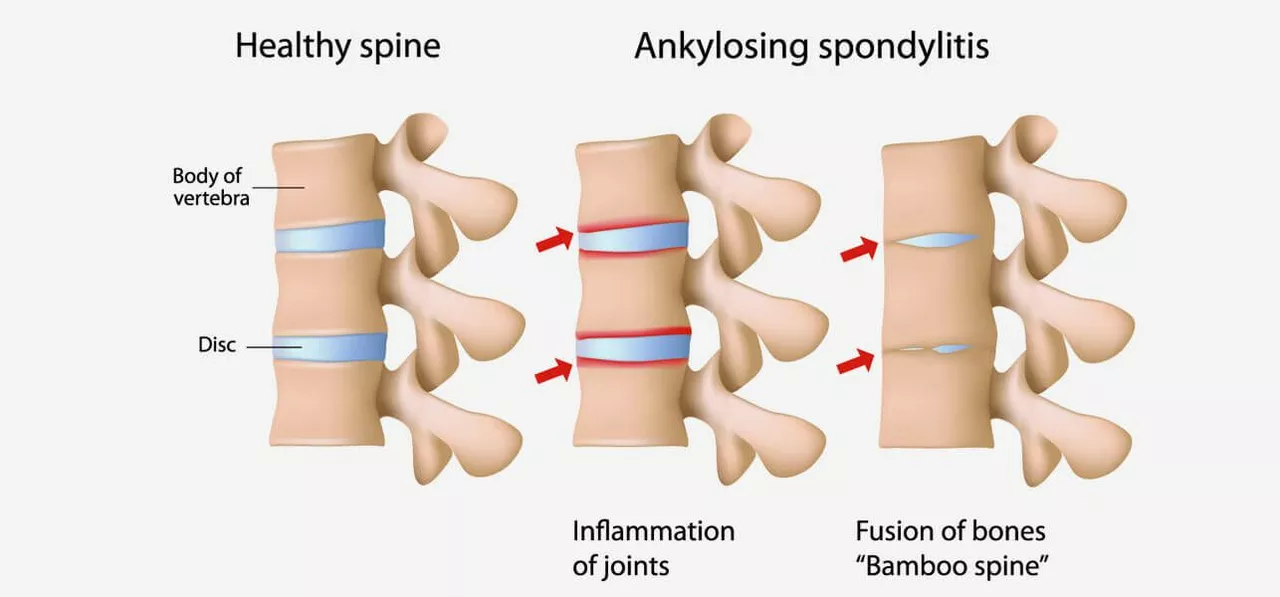
Sulfasalazine for Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Comprehensive Review
I recently came across a comprehensive review on the use of Sulfasalazine for treating Ankylosing Spondylitis (AS), a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the spine. The review highlights that Sulfasalazine has been widely used as an effective treatment for AS and helps in reducing pain, improving mobility, and slowing down the progression of the disease. It also emphasizes the importance of early intervention and proper dosage for achieving the best possible results. Though Sulfasalazine is generally considered safe, the review also mentions potential side effects that one should be aware of. Overall, the review provides valuable insights for patients and healthcare professionals alike who are dealing with Ankylosing Spondylitis.
read more