Calcium Carbonate in Industry: Practical Uses in Batteries and Oil & Gas
Have you noticed calcium carbonate popping up in tech and energy news? It’s not just chalk — this mineral shows real value in batteries and oil & gas work. Below I explain where it’s used, why manufacturers choose it, and what to watch for when picking a grade or supplier.
Batteries: cheap, stable, and useful
In battery making, calcium carbonate usually works as a filler and structural additive. In lithium-ion and other electrode mixes, fine calcium carbonate helps control porosity and improves mechanical strength. That means electrodes hold together better through charge cycles and handling.
It also cuts cost. Replacing part of the active material with a stable, low-cost filler lowers raw material spend without wrecking performance. Producers often choose precipitated calcium carbonate (PCC) for batteries because its particle size and shape are more consistent than ground limestone.
Another role is in separator coatings and binders. A thin layer with calcium carbonate can improve wetting and electrolyte distribution, which helps ion flow. For manufacturers focused on scaling production, this mineral is attractive: reliable supply, simple processing, and fewer regulatory headaches compared with specialty additives.
Oil & gas: drilling, sealing, and stabilizing
On rigs, calcium carbonate shines as a multi-tasker. It’s a common weighting and bridging agent in drilling fluids. When a well has fractured zones or lost-circulation paths, crushed or engineered calcium carbonate particles lodge in pores and fractures to seal leaks. That cuts non-productive time and keeps drilling on schedule.
Calcium carbonate also helps keep drilling fluid density stable and neutralizes acids during well treatments. In cementing, it can adjust properties to improve set and reduce shrinkage. Because it’s chemically inert in many conditions, operators often prefer it to reactive alternatives that can cause side reactions downhole.
Grade matters here. Coarse, angular particles work better for bridging large losses; fine, rounded PCC fits well where controlled fluid rheology and suspension are key. Matching particle distribution to the problem makes a big difference in field results.
How to pick the right calcium carbonate? First, match particle size and hardness to the application: batteries need consistent, fine PCC; drilling needs tailored blends. Check purity and contaminants — heavy metals or sulfates can cause problems in electrochemistry or drilling chemistry. Ask suppliers for batch certificates and particle-size analyses.
Also think about sustainability and supply chain. Many manufacturers prefer sources with steady production and traceable mining practices. Recycled or low-impact PCC options are available and may fit projects that want lower carbon footprints.
Want a quick checklist? Choose the right grade (PCC vs GCC), confirm particle-size distribution, verify purity, and confirm steady delivery. That simple process keeps batteries reliable and rigs running without surprises.
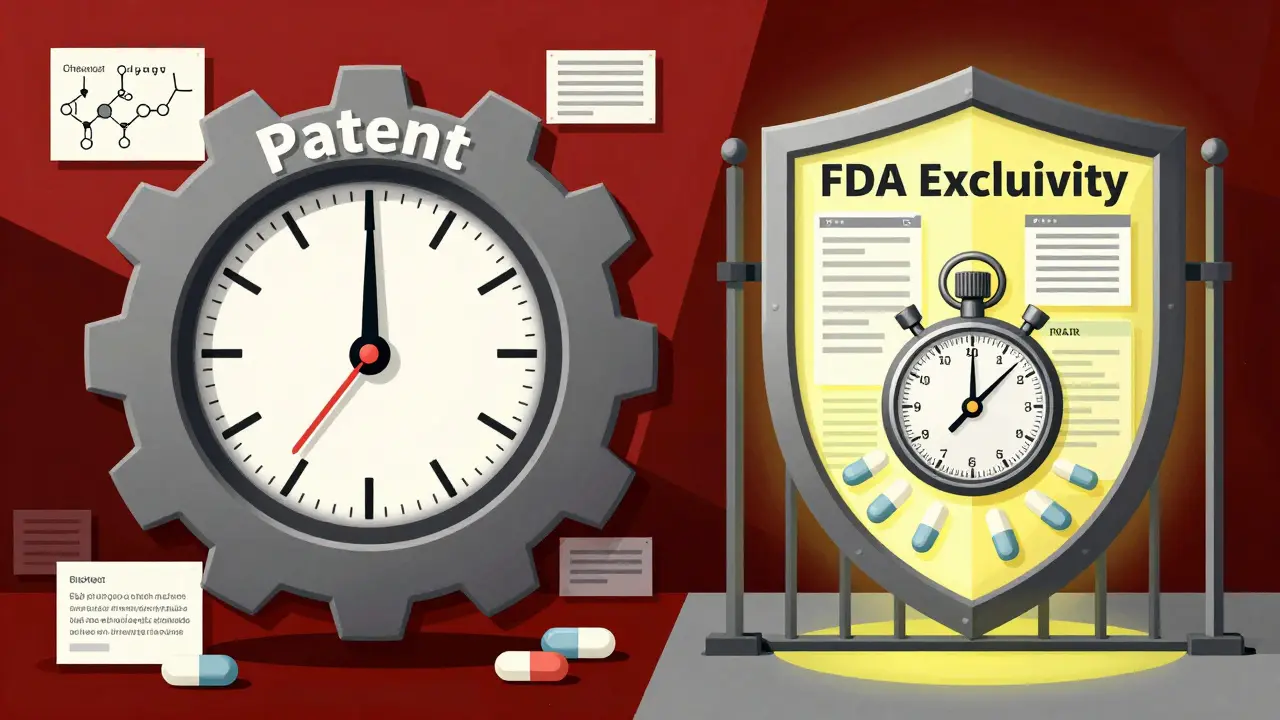
Patent Exclusivity vs Market Exclusivity: What’s the Real Difference for Drug Prices?
Patent exclusivity and market exclusivity are two separate legal tools that protect drug prices. Patents cover inventions; FDA exclusivity blocks generics using clinical data-even without a patent. Understanding the difference explains why some drugs stay expensive long after patents expire.
read more
How DTC Advertising Shapes Patient Perceptions of Generic Medications
DTC prescription drug ads in the U.S. drive higher demand for branded medications, often overshadowing equally effective generics. Research shows ads increase prescriptions but also lead to inappropriate requests and higher costs. Learn how advertising influences patient decisions and healthcare outcomes.
read more
IVIVC and Waivers: How In Vitro Methods Are Replacing In Vivo Bioequivalence Testing
IVIVC lets pharmaceutical companies predict how a drug behaves in the body using lab-based dissolution tests, replacing costly and time-consuming human trials. When done right, it saves millions and speeds up generic drug approval.
read more
Contamination Controls: Preventing Adulteration in Generic Drug Manufacturing
Contamination controls in generic drug manufacturing prevent harmful adulteration through cleanroom standards, real-time monitoring, and strict cleaning protocols. Learn how facilities avoid cross-contamination and meet FDA requirements.
read more
The use of calcium carbonate in the production of batteries
As a blogger researching the latest advancements in battery technology, I recently discovered the significant role calcium carbonate plays in the production of batteries. Calcium carbonate serves as a crucial component in the manufacturing process, contributing to improved performance and increased energy storage capacity. It also aids in reducing the overall cost of production, making batteries more affordable for consumers. Additionally, calcium carbonate's eco-friendly nature makes it a sustainable choice in the quest for developing cleaner energy sources. Overall, calcium carbonate is revolutionizing the battery industry, paving the way for a greener and more efficient future.
read more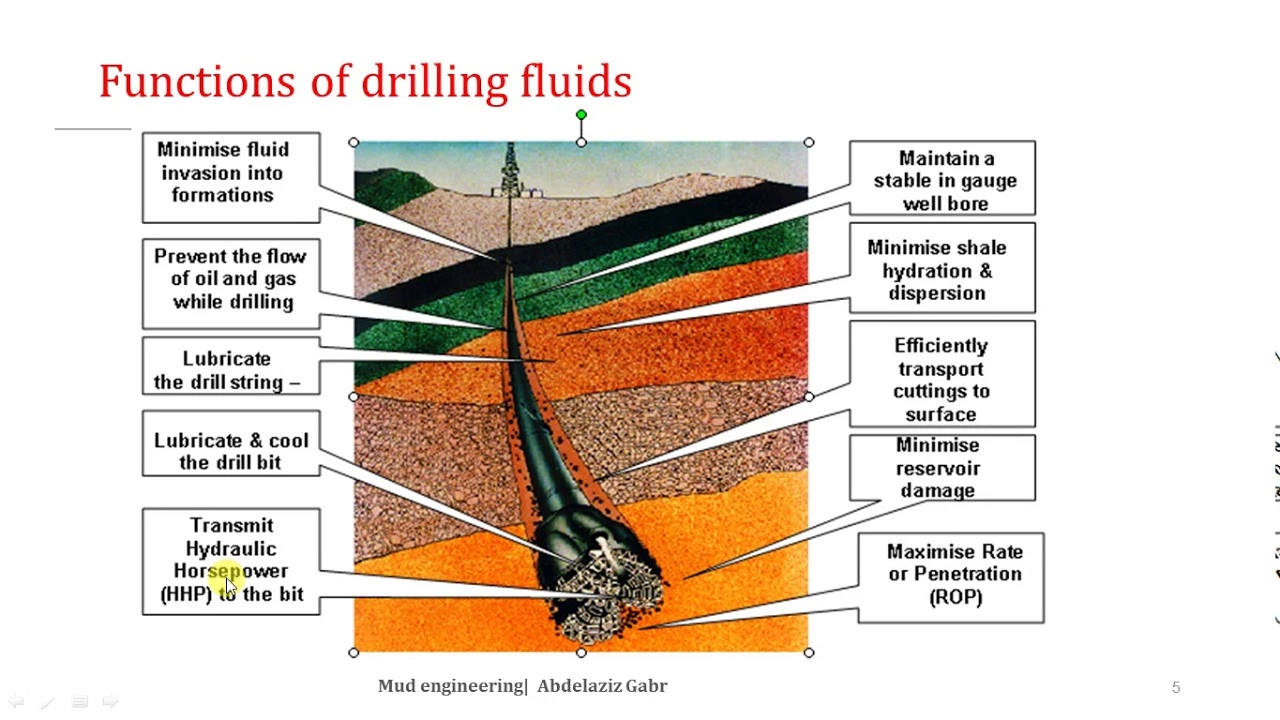
Calcium carbonate in the oil and gas industry: An essential component
As a vital component in the oil and gas industry, calcium carbonate plays a crucial role in various aspects of the drilling process. It helps in stabilizing the drilling fluid, preventing the formation of gas hydrates, and maintaining the desired density of the fluid. Additionally, calcium carbonate is an effective bridging agent, sealing off porous sections of the wellbore to prevent fluid loss. Furthermore, it aids in the neutralization of acidic components in the drilling fluid, ensuring the well's stability and safety. Overall, calcium carbonate's versatility and effectiveness make it an indispensable component in the oil and gas industry.
read more